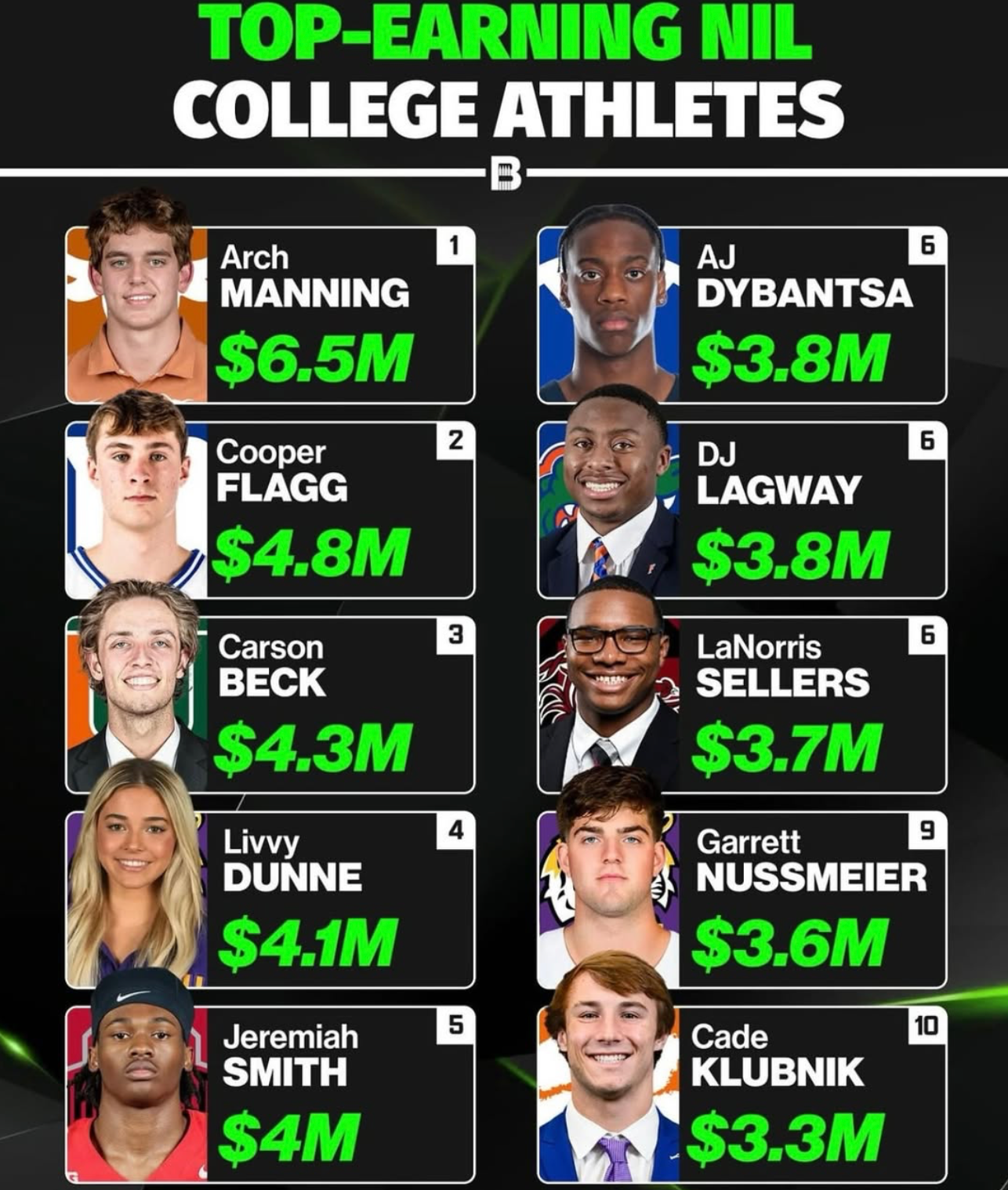
The House Settlement: A New Era of Athlete Compensation

The House v. NCAA settlement represents a landmark shift in collegiate athletics. Pending final approval, this $2.8 billion agreement addresses antitrust lawsuits concerning restrictions on athletes' ability to profit from their NIL. Key components of the settlement include:
- Backpay for Athletes: Approximately $2.78 billion will be distributed to athletes who competed between 2016 and 2024, compensating for previous NIL restrictions.
- Revenue Sharing Model: Starting July 1, 2025, schools can allocate up to $20.5 million annually to athletes, equating to about 22% of their athletic revenue.
- Enhanced Athlete Benefits: Beyond financial compensation, athletes will gain access to improved mental health resources, nutritional support, life skills development, and extended medical coverage post-competition.
While the settlement marks progress, it also raises concerns regarding equitable distribution, particularly for non-revenue sports and female athletes. Critics argue that the revenue-sharing model may not adequately address these disparities. Ave Maria School of Law
Transfer Portal Reforms: Increased Mobility for Athletes
The NCAA has implemented significant changes to transfer portal regulations, enhancing athlete mobility:
- Immediate Eligibility: Athletes meeting academic standards are now eligible to compete immediately upon transferring, regardless of the number of transfers.
- Defined Transfer Windows: Transfer periods have been standardized, with football's fall window opening for 20 days post-conference championships and a 10-day spring window in mid-April.
These reforms aim to provide athletes with greater flexibility while maintaining competitive balance across programs.
NIL Dynamics: Navigating the New Frontier
The NIL landscape continues to evolve, introducing both opportunities and complexities:
- Third-Party Deals: Athletes can engage in endorsement deals with third parties, supplementing income beyond institutional revenue sharing.
- Regulatory Oversight: To ensure transparency, the NCAA is developing systems to monitor NIL agreements exceeding $600, aiming to prevent circumvention of compensation caps.
However, disparities in NIL opportunities persist, often favoring high-profile sports and athletes, prompting ongoing discussions about fairness and equity.
Institutional Adaptations: Embracing the New Landscape
Universities are proactively adjusting to these changes. For instance, Clemson University plans to fully fund the NCAA settlement and increase scholarships across all sports, integrating fundraising efforts with donor incentives to support athlete compensation.
Such initiatives reflect a broader trend of institutions seeking innovative solutions to remain competitive and compliant in the evolving collegiate athletic environment.
Conclusion: Charting the Future of College Athletics
The intersection of the House settlement, transfer portal reforms, and NIL advancements signifies a transformative period in NCAA sports. While these developments offer enhanced opportunities for athletes, they also necessitate careful navigation to address emerging challenges related to equity, compliance, and sustainability.
As stakeholders adapt to this new era, the focus remains on fostering an environment that balances athlete empowerment with the integrity and viability of collegiate athletics.